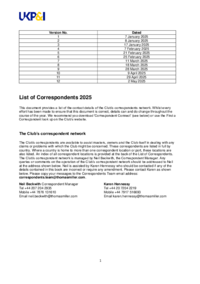
1648 results:
Date: 2 May 2025
Date: 2 May 2025
Date: 1 May 2025
Date: 29 April 2025
Date: 28 April 2025
Date: 28 April 2025
Date: 28 April 2025
Date: 24 April 2025
Date: 23 April 2025
Date: 23 April 2025